This example has been auto-generated from the examples/ folder at GitHub repository.
Gamma Mixture Model
# Activate local environment, see `Project.toml`
import Pkg; Pkg.activate(".."); Pkg.instantiate();This notebook implements one of the experiments outlined in https://biaslab.github.io/publication/mp-based-inference-in-gmm/.
Load packages
using RxInfer, Random, StatsPlots# create custom structure for model parameters for simplicity
struct GammaMixtureModelParameters
nmixtures # number of mixtures
priors_as # tuple of priors for variable a
priors_bs # tuple of priors for variable b
prior_s # prior of variable s
endModel specification
@model function gamma_mixture_model(y, parameters)
# fetch information from struct
nmixtures = parameters.nmixtures
priors_as = parameters.priors_as
priors_bs = parameters.priors_bs
prior_s = parameters.prior_s
# set prior on global selection variable
s ~ Dirichlet(probvec(prior_s))
# allocate variables for mixtures
local as
local bs
# set priors on variables of mixtures
for i in 1:nmixtures
as[i] ~ Gamma(shape = shape(priors_as[i]), rate = rate(priors_as[i]))
bs[i] ~ Gamma(shape = shape(priors_bs[i]), rate = rate(priors_bs[i]))
end
# allocate variables for local selection variable
local z
# specify local selection variable and data generating process
for i in 1:length(y)
z[i] ~ Categorical(s)
y[i] ~ GammaMixture(switch = z[i], a = as, b = bs)
end
endconstraints = @constraints begin
q(z, as, bs, s) = q(z)q(as)q(bs)q(s)
q(as) = q(as[begin])..q(as[end])
q(bs) = q(bs[begin])..q(bs[end])
q(as)::PointMassFormConstraint(starting_point = (args...) -> [1.0])
endConstraints:
q(z, as, bs, s) = q(z)q(as)q(bs)q(s)
q(as) = q(as[(begin)..(end)])
q(bs) = q(bs[(begin)..(end)])
q(as) :: PointMassFormConstraint()# specify seed and number of data points
rng = MersenneTwister(43)
n_samples = 2500
# specify parameters of mixture model that generates the data
# Note that mixture components have exactly the same means
mixtures = [ Gamma(9.0, inv(27.0)), Gamma(90.0, inv(270.0)) ]
nmixtures = length(mixtures)
mixing = rand(rng, nmixtures)
mixing = mixing ./ sum(mixing)
mixture = MixtureModel(mixtures, mixing)
# generate data set
dataset = rand(rng, mixture, n_samples);# specify priors of probabilistic model
# NOTE: As the means of the mixtures "collide", we specify informative prior for selector variable
nmixtures = 2
gpriors = GammaMixtureModelParameters(
nmixtures, # number of mixtures
[ Gamma(1.0, 0.1), Gamma(1.0, 1.0) ], # priors on variables a
[ GammaShapeRate(10.0, 2.0), GammaShapeRate(1.0, 3.0) ], # priors on variables b
Dirichlet(1e3*mixing) # prior on variable s
)
gmodel = gamma_mixture_model(parameters = gpriors)
gdata = (y = dataset, )
init = @initialization begin
q(s) = gpriors.prior_s
q(z) = vague(Categorical, gpriors.nmixtures)
q(bs) = GammaShapeRate(1.0, 1.0)
end
greturnvars = (s = KeepLast(), z = KeepLast(), as = KeepEach(), bs = KeepEach())
goptions = (
default_factorisation = MeanField() # Mixture models require Mean-Field assumption currently
)
gresult = infer(
model = gmodel,
data = gdata,
constraints = constraints,
options = (limit_stack_depth = 100,),
initialization = init,
returnvars = greturnvars,
free_energy = true,
iterations = 250,
showprogress = true
);# extract inferred parameters
_as, _bs = mean.(gresult.posteriors[:as][end]), mean.(gresult.posteriors[:bs][end])
_dists = map(g -> Gamma(g[1], inv(g[2])), zip(_as, _bs))
_mixing = mean(gresult.posteriors[:s])
# create model from inferred parameters
_mixture = MixtureModel(_dists, _mixing);# report on outcome of inference
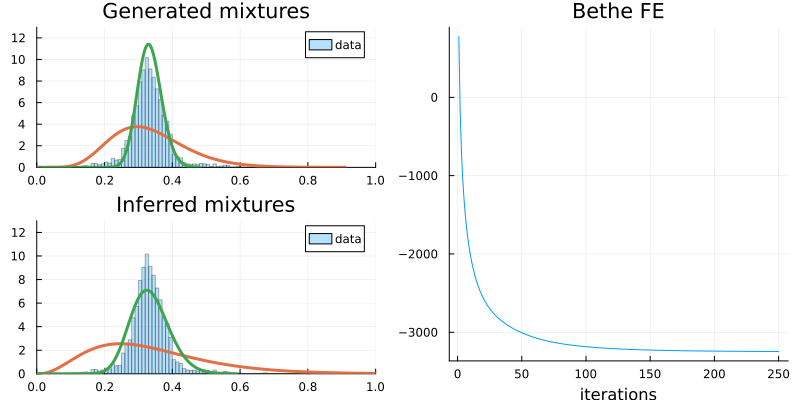
println("Generated means: $(mean(mixtures[1])) and $(mean(mixtures[2]))")
println("Inferred means: $(mean(_dists[1])) and $(mean(_dists[2]))")
println("========")
println("Generated mixing: $(mixing)")
println("Inferred mixing: $(_mixing)")Generated means: 0.3333333333333333 and 0.33333333333333337
Inferred means: 0.34033857782340327 and 0.3343339085733581
========
Generated mixing: [0.18923488676601088, 0.8107651132339891]
Inferred mixing: [0.11673110542151635, 0.8832688945784838]# plot results
p1 = histogram(dataset, ylim = (0, 13), xlim = (0, 1), normalize=:pdf, label="data", opacity=0.3)
p1 = plot!(mixture, label=false, title="Generated mixtures", linewidth=3.0)
p2 = histogram(dataset, ylim = (0, 13), xlim = (0, 1), normalize=:pdf, label="data", opacity=0.3)
p2 = plot!(_mixture, label=false, title="Inferred mixtures", linewidth=3.0)
# evaluate the convergence of the algorithm by monitoring the BFE
p3 = plot(gresult.free_energy, label=false, xlabel="iterations", title="Bethe FE")
plot(plot(p1, p2, layout = @layout([ a; b ])), plot(p3), layout = @layout([ a b ]), size = (800, 400))